GUIプログラム:講義資料を参考に、以下の課題を行え。{〜01/15(Mon)}
1 偶数奇数判定プログラム(GUIaa)をタイプし、その動作を考察せよ。
2 例外処理について、考察せよ。
3 上述のサンプルプログラムに出てきたGUI部品を、全て使ったプログラムを作成せよ。
4 摂氏から華氏、華氏から摂氏への温度換算ができるプログラムを作成せよ。。
5「電卓」プログラム。中身は自分の思うように。
ソースコード
1 import java.awt.*;
2 import java.awt.event.*;
3
4 public class hantei extends Frame {
5 Button b0 = new Button("偶数/奇数?");
6 Label x0 = new Label("数字を入力");
7 TextField t0 = new TextField();
8
9 public hantei() {
10 setLayout(null);
11 add(t0); t0.setBounds(10, 40, 90, 30);
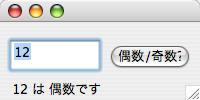
12 add(b0); b0.setBounds(110, 40, 80, 30);
13 add(x0); x0.setBounds(10, 80, 180, 30);
14 b0.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
15 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
16 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
17 t0.setText("");
18 if(i % 2 == 0) {
19 x0.setText(i + " は 偶数です");
20 } else {
21 x0.setText(i + " は 奇数です");
22 }
23 }
24 });
25 }
26 public static void main(String[] args) {
27 Frame win = new hantei();
28 win.setSize(200, 100); win.setVisible(true);
29 win.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
30 public void windowClosing(WindowEvent evt) {
31 System.exit(0);
32 }
33 });
34 }
35 }
|
実行結果
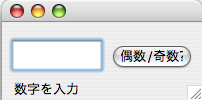
数字を入力すると
try {
…例外が発生する可能性のある処理…
} catch(Exception ex) {
…例外時の処理…
}
finally {
…finallyブロック…
}
|
ソースコード
1 import java.awt.*;
2 import java.awt.event.*;
3
4 public class gui extends Frame {
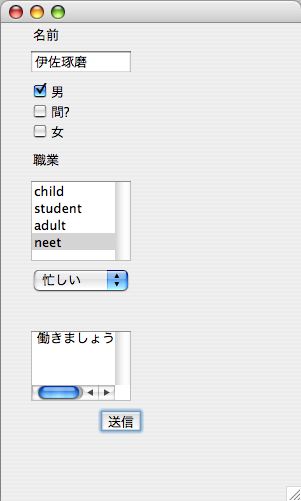
5 Button b0 = new Button("送信");
6 Label x0 = new Label("職業");
7 Label x1 = new Label("名前");
8 Label x2 = new Label("今日");
9 TextField t0 = new TextField();
10 Checkbox ch0 = new Checkbox("男");
11 Checkbox ch1 = new Checkbox("間??");
12 Checkbox ch2 = new Checkbox("女");
13 List l1 = new List();
14 Choice c1 = new Choice();
15 TextArea ta0 = new TextArea("TextArea");
16 public gui() {
17 setLayout(null);
18 add(b0); b0.setBounds(100,410,40,20);
19 add(x1); x1.setBounds(30,25,40,20);
20 add(t0); t0.setBounds(30,50,100,20);
21 add(x0); x0.setBounds(30,150,40,20);
22 add(ch0); ch0.setBounds(30,80,40,20);
23 add(ch1); ch1.setBounds(30,100,40,20);
24 add(ch2); ch2.setBounds(30,120,40,20);
25 add(l1); l1.setBounds(30,180,100,80);
26 l1.add("child"); l1.add("student"); l1.add("adult");l1.add("neet"); 27 add(c1); c1.setBounds(30,240,100,80);
28 c1.add("忙しい"); c1.add("暇");c1.add("寝る");
29 add(ta0);ta0.setBounds(30,330,100,70);
30 b0.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
31 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt){
32 ta0.setText("働きましょう");
33 }
34 });
35 }
36 public static void main(String[] args) {
37 Frame win = new gui();
38 win.setSize(300, 500);
39 win.setVisible(true);
40 }
41 };
|
実行結果
アンケート
ソースコード
1 import java.awt.*;
2 import java.awt.event.*;
3
4 public class ondo extends Frame{
5
6 Button b0 = new Button("摂氏→華氏");
7 Button b1 = new Button("華氏→摂氏");
8 Label x0 = new Label("数字を入力");
9 TextField t0 = new TextField();
10 TextField t1 = new TextField();
11
12 public ondo(){
13 setLayout(null);
14 add(t0); t0.setBounds(75,50,50,20);
15 add(b0); b0.setBounds(20,110,80,20);
16 add(b1); b1.setBounds(100,110,80,20);
17 add(t1); t1.setBounds(75,145,50,20);
18 add(x0); x0.setBounds(60,80,160,20);
19
20 b0.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
21 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
22 try{
23 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
24 t1.setText(""+(i*1.8+32));
25 }catch(Exception ex){
26 t1.setText("error");
27 }
28 }
29 });
30
31 b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
32 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
33 try{
34 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
35 t1.setText(""+(i-32)/1.8);
36 }catch(Exception ex){
37 t1.setText("error");
38 }
39 }
40 });
41 }
42
43 public static void main(String[] args) {
44 Frame win = new ondo();
45 win.setSize(200, 200); win.setVisible(true);
46 win.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
47 public void windowClosing(WindowEvent evt) {
48 System.exit(0);
49 }
50 });
51 }
52 }
|
実行結果
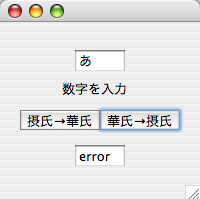
考察
動作としては最初にやった偶数奇数判定プログラムとだいたい似ている。ボタンを押したときの動きが違う
だけであとのソースはほとんど似たような設定になっている。あと例外処理も付け加えたので文字などを入
力すると「error」と表示される。華氏から摂氏にするときは、華氏の値に1.8をかけて32を足すことで摂
氏になる。摂氏から華氏にするには32を引いて1.8をかける。電卓プログラム
ソースコード
1 import java.awt.*;
2 import java.awt.event.*;
3 public class dentaku extends Frame {
4 Button b0 = new Button("+");
5 Button b1 = new Button("-");
6 Button b2 = new Button("*");
7 Button b3 = new Button("/");
8 Label l0 = new Label("電卓");
9 Label l1 = new Label("数字を入力");
10 Label l2 = new Label("結果");
11 TextField t0 = new TextField();
12 TextField t1 = new TextField();
13 TextField t2 = new TextField();
14 public dentaku() {
15 setLayout(null);
16 add(l0); l0.setBounds(125,30,50,20);
17 add(l1); l1.setBounds(115,60,70,20);
18 add(t0); t0.setBounds(125,90,50,20);
19 add(b0); b0.setBounds(100,120,50,20);
20 add(b1); b1.setBounds(150,120,50,20);
21 add(b2); b2.setBounds(100,140,50,20);
22 add(b3); b3.setBounds(150,140,50,20);
23 add(t1); t1.setBounds(125,170,50,20);
24 add(l2); l2.setBounds(125,200,50,20);
25 add(t2); t2.setBounds(125,230,50,20);
26 b0.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
27 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
28 try {
29 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
30 int k = (new Integer(t1.getText())).intValue();
31 t2.setText("" + (i+k) + "");
32 }catch(NumberFormatException ne) {
33 l0.setText(" error");
34 }
35 }
36 });
37 b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
38 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
39 try {
40 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
41 int k = (new Integer(t1.getText())).intValue();
42 t2.setText("" + (i-k) + "");
43 }catch(Exception ne) {
44 l0.setText(" error");
45 }
46 }
47 });
48 b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
49 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
50 try {
51 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
52 int k = (new Integer(t1.getText())).intValue();
53 t2.setText("" + i*k + "");
54 }catch(Exception ne){
55 l0.setText(" error");
56 }
57 }
58 });
59 b3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
60 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
61 try {
62 int i = (new Integer(t0.getText())).intValue();
63 int k = (new Integer(t1.getText())).intValue();
64 t2.setText("" + i/k + "");
65 }catch(Exception ne) {
66 l0.setText(" error");
67 }
68 }
69 });
70
71 }
72 public static void main(String[] args) {
73 Frame win = new dentaku();
74 win.setSize(300,300);
75 win.setVisible(true);
76 win.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
77 public void windowClosing(WindowEvent evt) {
78 System.exit(0);
79 }
80 });
81 }
82 }
|
実行結果